由于工作项目的关系,有机会学习和使用微软的虚拟化软件Hyper-V。由于Hyper-V是个纯商用的软件项目,不像开源的KVM有全部的代码和充足的文档可供阅读,所以目前也是根据官网的仅有的一些介绍性文档和网络资源、部分开源代码进行了学习,此处进行记录,若有不对之处,可以留言、邮件进行探讨。
Hypervisor的分类
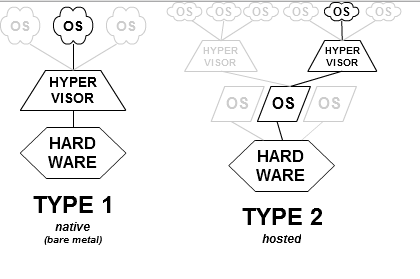
开始深入Hyper-V之前,有必要了解下Hypervisor的技术分类,在Hypervisor技术的发展过程中,各自采用的架构和理念也不尽相同,大致分为两类,详细见 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypervisor
Type-1, native or bare-metal hypervisors
这种Hypervisor直接运行在host的hardware上控制所有的硬件资源并管理Guest OS.
这种代表性的虚拟化产品包括:Oracle VM Server for SPARC, Oracle VM Server for x86, the Citrix XenServer, Microsoft’s Hyper-V, and VMware ESX/ESXi.
Type-2 or hosted hypervisors
这种Hypervisor像普通的程序一样运行在传统的OS中,该种Hypervisor将Guest抽象于Host进行管理。
这种代表性的虚拟化产品包括:VMware Workstation, VMware Player, VirtualBox and QEMU.
然而这两种技术的界定并没有那么清楚的区分,Linux的KVM和FreeBSD的bhyve都作为内核模块将Host OS转换成Type-1 Hypervisor。
同时,Linux和FreeBSD仍是作为通用操作系统与其他应用程序竞争VM资源,所以KVM和bhyve可以被分类至成Type-2 Hypervisor
由上论述及下图可见hyper-v与KVM从技术角度看是完全两种不同的路线。
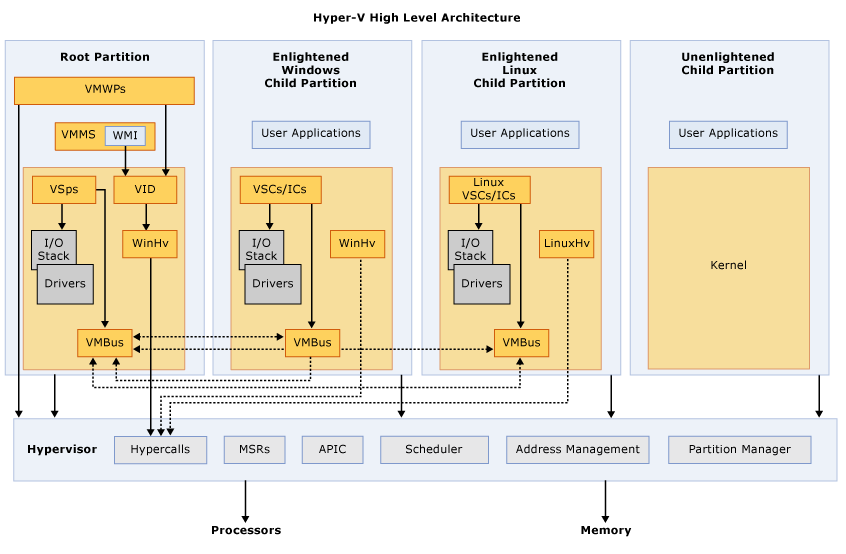
hyper-v的架构
Hyper-V是一种针对x64 versions of Windows Server 2008以及更高版本的基于hypervisor的虚拟化技术。和其它Hypervisor一样,其也支持多个OS的隔离并共享hardware资源。
Hyper-V支持隔离性主要是使用了一个称为“partition”的概念。一个partition是一个独立逻辑单元。Hyper-V的运行必须至少拥有一个parent或root的partition,虚拟栈运行在parent的partition中,拥有直接访问硬件设备的能力。Parent partition用来创建child partition,这里就是指Guest OS。
Partition不能直接访问物理处理器,不能处理处理器中断,而是Hypervisor来接管处理,并重定向到指定的partition,Hyper-V和KVM一样,也提供了IOMMU来提高IO的性能。
Child partition不能直接访问硬件设备,而是通过vmbus或者Hypervisor来访问处于parent partition中的设备,VMBus则是partition之间的内部通信通道。
VSPs(Virtualization Service Providers)位于parent partition中,接收来自于child partition的request。
VSCs(Virtualization Client Providers)位于child partition中,通过VMBus重定向对dev的request到VSPs。
Linux Integration Services(LIS)
回到2008年,当微软意识到其在虚拟化技术和云服务上已落后,公司的一部分研发资源就投入到了Hyper-V虚拟化环境。而最开始的时候Hyper-V只支持Windows client systems. Redmond不久意识到对Linux支持的重要性,2009年开始支持Linux Guest,然而仅提供Linux虚拟机的基础性的功能是不够的,为具备竞争力,微软投入了更多的研发资源来提高Linux guest的performance.
LIS(Linux Integration Services)就是当时为Linux虚拟化提供更好,更快,更多集成服务的软件产品。LIS类似运行在ESX Server上的VMware tools。
Understanding LIS
LIS的运行形式为运行在Host和Guest中的一组系统级driver。其提供了两种类型的组件:
- Driver
- Services
Driver通过支持guest对Host的直接访问来增强系统的整体性能。比如VMBus Driver通过减少Guest和Host之间的层次结构来减少通信消耗。
Services则提供了特定的服务功能,例如Guest和Host的时间同步服务。
LIS提供的driver
- VMBus
- VSP/VSC
- SCSI Driver
- IDE Driver
- VMBus Network Controller Drivers
- Hyper-V Balloon Driver
- HID-Compatible Mouse Driver
LIS提供的services
- Time Synchronization
- Guest Shutdown
- Heartbeat
- Data Exchange
具备LIS能力的Guest在Hyper-V的架构中可以称为Enlightened. 我的理解其类似于Para Virtualization. 通过一组特定的半虚拟化驱动来提高整体性能, LIS的driver直接类比于virtio。
代码部分
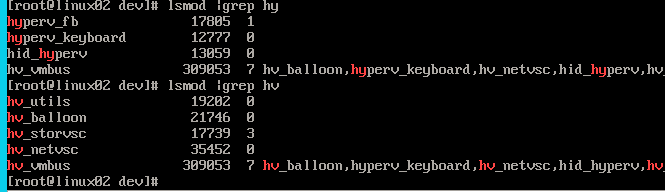
目前Linux内核主线代码已经全部支持LIS,且默认使能,当在Hyper-V上install Linux的发行版,比如Ubuntu后,就能看到LIS驱动的各类设备。
在Linux内核中的各类驱动可以理解为类似virtio的前端代码。
代码主要集中在如下:
1 | drivers\hv 主要是VMBus driver,channel管理,ring buffer的相关code |
LIS Driver code在Linux内核中必然遵循的是Linux Driver开发的体系结构:Bus、Device、Driver。
VMBus作为一种总线(bus)注册,可以类比为PCI,而net,ide,scsi,ballon做为device注册,hv_netvsc/hv_storvsc/hv_ballon作为driver注册。
下面是code阅读记录,参看图,流程不过多赘述,主要说明几个Hyper-V相关的特定操作。
Hypervisor的检测
Linux初始化时会对支持的Hypervisor进行检测,调用指定的平台处理函数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47static const __initconst struct hypervisor_x86 * const hypervisors[] =
{
&x86_hyper_xen_hvm,
&x86_hyper_vmware,
&x86_hyper_ms_hyperv, <--------------------
&x86_hyper_kvm,
};
const __refconst struct hypervisor_x86 x86_hyper_ms_hyperv = {
.name = "Microsoft HyperV",
.detect = ms_hyperv_platform,
.init_platform = ms_hyperv_init_platform,
};
static inline void __init
detect_hypervisor_vendor(void)
{
const struct hypervisor_x86 *h, * const *p;
uint32_t pri, max_pri = 0;
for (p = hypervisors; p < hypervisors + ARRAY_SIZE(hypervisors); p++) {
h = *p;
pri = h->detect();
if (pri != 0 && pri > max_pri) {
max_pri = pri;
x86_hyper = h;
}
}
}
void __init init_hypervisor_platform(void)
{
detect_hypervisor_vendor();
if (!x86_hyper)
return;
init_hypervisor(&boot_cpu_data);
if (x86_hyper->init_platform)
x86_hyper->init_platform();
}
hypercall
在Hyper-V中,Guest到Hypervisor的消息传递通过hypercall来实现,hypercall有message和event两种类型。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19/* Declare the various hypercall operations. */
enum hv_call_code {
HVCALL_POST_MESSAGE = 0x005c,
HVCALL_SIGNAL_EVENT = 0x005d,
};
static u64 do_hypercall(u64 control, void *input, void *output)
{
u64 hv_status = 0;
u64 input_address = (input) ? virt_to_phys(input) : 0;
u64 output_address = (output) ? virt_to_phys(output) : 0;
void *hypercall_page = hv_context.hypercall_page;
__asm__ __volatile__("mov %0, %%r8" : : "r" (output_address) : "r8");
__asm__ __volatile__("call *%3" : "=a" (hv_status) :
"c" (control), "d" (input_address),
"m" (hypercall_page));
}
共享page
Guest与Hypervisor的数据传输则通过共享page来实现。
例如vmconnection中的interrupt state page, monitor page, VMBus channel中的ring buffer, hv_netvsc driver中的recv buffer.
通过vmbus_establish_gpadl建立guest physical address description list. 将gpadlmsg使用hypercall通告hypervisor。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25/*
* vmbus_establish_gpadl - Estabish a GPADL for the specified buffer
*
* @channel: a channel
* @kbuffer: from kmalloc or vmalloc
* @size: page-size multiple
* @gpadl_handle: some funky thing
*/
int vmbus_establish_gpadl(struct vmbus_channel *channel, void *kbuffer,
u32 size, u32 *gpadl_handle)
{
...
next_gpadl_handle = atomic_read(&vmbus_connection.next_gpadl_handle);
atomic_inc(&vmbus_connection.next_gpadl_handle);
...
ret = create_gpadl_header(kbuffer, size, &msginfo, &msgcount);
...
gpadlmsg = (struct vmbus_channel_gpadl_header *)msginfo->msg; <---组装gpadl msg
gpadlmsg->header.msgtype = CHANNELMSG_GPADL_HEADER;
gpadlmsg->child_relid = channel->offermsg.child_relid;
gpadlmsg->gpadl = next_gpadl_handle;
...
vmbus_post_msg(gpadlmsg, msginfo->msgsize - sizeof(*msginfo));
...
}
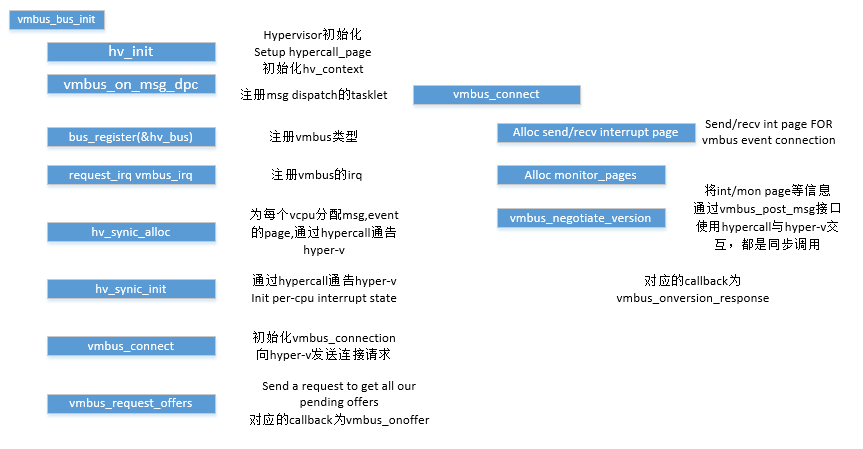
code walk through
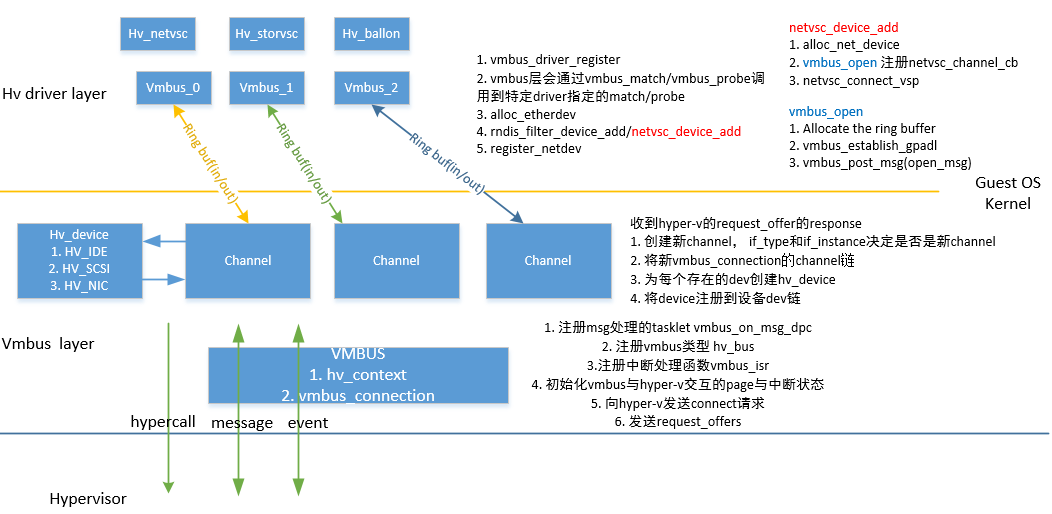
VMBus的初始化
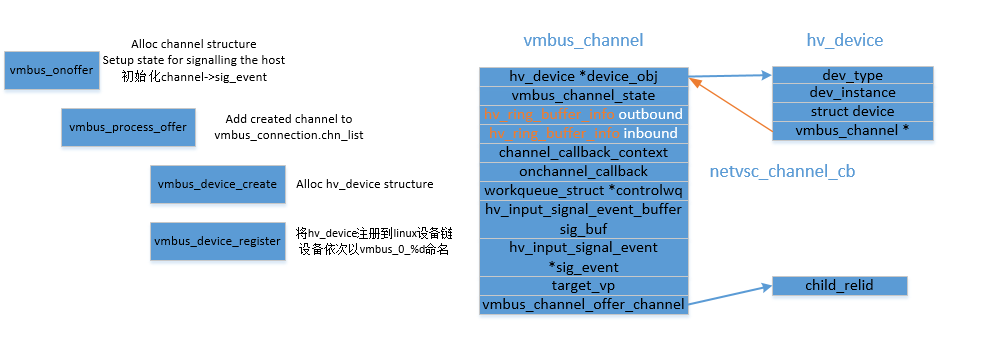
HV设备的注册
整体架构
参考文档
- https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc768520(v=bts.10).aspx.aspx)
- http://www.virtuatopia.com/index.php/An_Overview_of_the_Hyper-V_Architecture
- http://kristiannese.blogspot.com/2011/01/what-about-vmbus-hyper-v-architecture.html
- http://www.linux-magazine.com/Issues/2014/158/Linux-Integration-Services
- https://github.com/LIS