Qcow2镜像格式是qemu支持的磁盘镜像格式之一,目前虚拟化中主流的镜像格式。
Terminology
| terminology | explain |
|---|---|
| cluster | 一个Qcow2 img文件由固定大小的单元组成,该单元称为cluster,默认大小为65536bytes/64K |
| sector | 数据块读写的最小单元,大小为512字节 |
| host cluster | 位于Host上qcow2 img文件的cluster管理名称 |
| guest cluster | Guest所看到的virtual disk的cluster管理名称 |
| Qcow2 Header | Qcow2 img的文件头信息,占用第一个cluster |
| refcount | Qcow2内部用于管理cluster的分配而维护的引用计数 |
| refcount table | 用于查找refcount的第一级表 |
| refcount block | 用于查找refcount的第二级表 |
| L1 table | 用于查找guest cluster到host cluster映射的第一级表 |
| L2 table | 用于查找guest cluster到host cluster映射的第二级表 |
| IBA | image block address |
| VBA | virtual block address |
Qcow2镜像的组成
Qcow2 Header
Qcow2 img头描述了这个img的一些相关信息,该头部占用一个cluster,固定存放在文件起始处。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23typedef struct QCowHeader {
uint32_t magic;
uint32_t version;
uint64_t backing_file_offset;
uint32_t backing_file_size;
uint32_t cluster_bits; //1 << cluster_bits is the cluster size
uint64_t size; /* in bytes */ //虚拟磁盘的大小
uint32_t crypt_method;
uint32_t l1_size; //L1表的entry数目
uint64_t l1_table_offset; //L1表在img中的偏移
uint64_t refcount_table_offset; //refcount table在img中的偏移
uint32_t refcount_table_clusters;//refcount table所占用的cluster数目
uint32_t nb_snapshots; //snapshot的个数
uint64_t snapshots_offset; //snapshot相对img file的offset
/* The following fields are only valid for version >= 3 */
uint64_t incompatible_features;
uint64_t compatible_features;
uint64_t autoclear_features;
uint32_t refcount_order;
uint32_t header_length; //sizeof(QCowHeader)
} QEMU_PACKED QCowHeader;
Qcow2 Host cluster management
Qcow2维护refcount用以管理image中cluster的分配和释放,refcount作用等同于引用计数,代表了指定的cluster的使用状态:
0: 表示空闲
1: 表示已使用
大于等于2:表示已使用并且写访问必须执行COW操作
refcounts通过二级表(类似页表)来进行索引,第一级表称为refcount table,其大小可变、连续、占用多个cluster,其表项中每一个条目为指向第二级表的指针(相对于img file的offset),每个条目占64bits。
第二级表称为refcount block,每个refcount block占用1个cluster,表中每个条目为2个字节大小的refcount。
给定一个相对于img file的offset可以通过下面计算关系得到refcount:1
2
3
4
5refcount_block_entries = (cluster_size / sizeof(uint16_t))
refcount_block_index = (offset / cluster_size) % refcount_table_entries
refcount_table_index = (offset / cluster_size) / refcount_table_entries
refcount_block = load_cluster(refcount_table[refcount_table_index]);
return refcount_block[refcount_block_index];
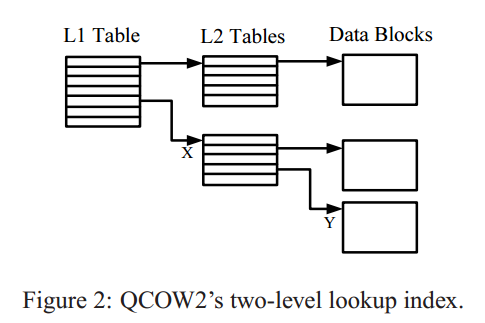
Qcow2 Cluster mapping(Guest->Host)
Guest OS看到的只是virtual disk,操作的是Guest Cluster,所以Qcow2镜像另个重要功能就是管理Guest Cluster到Host Cluster的映射。
Guest Cluster到Host Cluster的映射关系也是通过一个二级表来管理,称为L1表和L2表,L1表大小可变、连续、占用多个cluster,其表项中每一个条目为指向L2的指针(相对于img file的offset),每个条目占64bits。
L2表占用一个cluster,每个条目占64bits.
给定一个相对于virtual disk的offset,可以通过下面计算关系得到Host Cluster offset:1
2
3
4
5
6l2_entries = (cluster_size / sizeof(uint64_t))
l2_index = (offset / cluster_size) % l2_entries
l1_index = (offset / cluster_size) / l2_entries
l2_table = load_cluster(l1_table[l1_index]);
cluster_offset = l2_table[l2_index];
return cluster_offset + (offset % cluster_size)
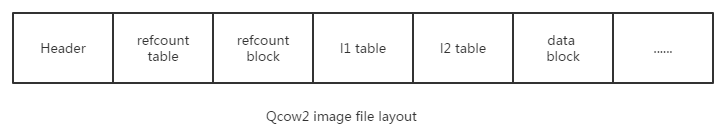
Qcow2 image file的布局
综合上述几个部分,可以看到Qcow2的大体布局,refcount table/refcount block/l1/l2的顺序关系不限
QEMU中关于Qcow2的实现
源码
Qcow2在qemu中的实现是作为块驱动实现,主要代码在:1
2
3
4
5block/qcow2.c
block/qcow2-refcount.c
block/qcow2-cluster.c
block/qcow2-snapshot.c
block/qcow2-cache.c
Qcow2镜像的创建
1 | $qemu-img create -f qcow2 test.qcow2 1G |
实现
Qcow2 img的操作在qemu中都是作为一种块设备的blockdriver来实现的,qcow2对应的bdrv_create注册的函数是qcow2_create,创建流程如下:1
2
3
4
5
6qcow2_create
qcow2_create2
bdrv_create_file
bdrv_create
bdrv_create_co_entry //qemu协程入口
raw_create
由于qcow2 image是以文件形式存在的,在Qcow2的底层仍需要通过文件操作写入实实在在的数据,在Qcow2管理结构上挂在了一个child管理结构,指向了bdrv_file的block driver,对应的API为raw_create,raw_open等。所以在层次划分上Qcow2 block driver完成了Qcow2内部格式的转换,比如Guest到host的cluster mapping,l1,l2表的建立,索引查找等。
在image file的创建流程上,首先写入header,offset为0,大小为cluster size
1 | blk_pwrite(blk, 0, header, cluster_size); |
接着写入一个refcount table和一个refcount block1
blk_pwrite(blk, cluster_size, refcount_table, 2 * cluster_size);
分配3个cluster,讲上面使用的3个cluster占用1
qcow2_alloc_clusters(blk_bs(blk), 3 * cluster_size);
最后根据header的最新信息更新image的header1
qcow2_update_header(blk_bs(blk));
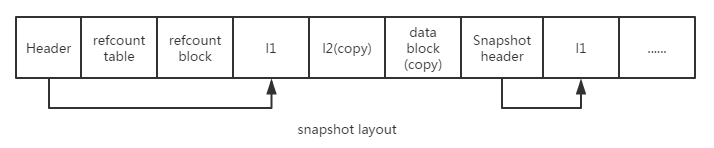
Qcow2 snapshot操作
Qcow2支持internal snapshots,即snapshot和base img存在一个单一的image file中。Qcow2对snapshot的操作主要转换为对L1表的切换。因为L1表能寻址到data block,不同的l1表对Guest展现不同的data block,这就是Qcow2 snapshot的基本实现原理。
snapshot相关的命令
1 | $qemu-img snapshot -c snapshot01 test.qcow2 //创建快照snapshot01 |
实现原理
下面是snapshot的header信息,每一个snapshot都有一个header,而header中的l1_table_offset标示了该snapshot所使用的l1表。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19typedef struct QEMU_PACKED QCowSnapshotHeader {
/* header is 8 byte aligned */
uint64_t l1_table_offset; //该snapshot所使用的l1表
uint32_t l1_size;
uint16_t id_str_size;
uint16_t name_size;
uint32_t date_sec;
uint32_t date_nsec;
uint64_t vm_clock_nsec;
uint32_t vm_state_size;
uint32_t extra_data_size; /* for extension */
/* extra data follows */
/* id_str follows */
/* name follows */
} QCowSnapshotHeader;
Create snapshot
1 | $qemu-img snapshot -c <snapshot-name> <imagename> |
qcow2_snapshot_create:
- 制造一个snapshot id;
- 分配snapshot header空间,填充信息;
- 分配l1表的空间,并从当前的image的l1表中copy;
- 将snapshot的l1表写入image file;
- 操作所有cluster的refcount,主要是l2表和data block的cluster;
- 增加refcount,并置cluster的状态的copied位;表明这些cluster在写操作是需执行COW;
- 将snapshot header写入image file;
List snapshot
1 | $qemu-img snapshot -l <imagename> |
Apply snapshot
1 | $qemu-img snapshot -a <snapshot-name> <imagename> |
qcow2_snapshot_goto:
主要操作就是切换snapshot的l1表为active;这样当有数据block的写入,寻址的都是snapshot的data block空间;
Delete snapshot
1 | $qemu-img snapshot -d <snapshot-name> <imagename> |
External snapshot
1 | $qemu-img create -b <imagename1> -f qcow2 -l <imagename2> |
此命令用于创建Qcow2的external snapshot,即snapshot和base img处于不同的image file中,此时base img就属于backing file;snapshot的空间不占用backing file的空间,而backing file退化成只读模板。